Provides services on dedicated infrastructure in various models, depending on customer needs.
Viettel Colocation
The colocation service with TIA-942 Rated 3 standards
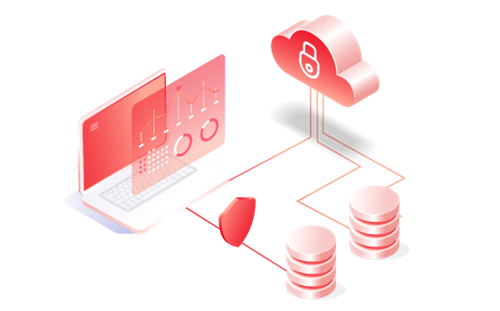
Provide a dedicated virtual server system using cloud computing technology, helping businesses ensure security, independence of resources, save hardware costs and optimize system administration.
In the Private Cloud, IT resources in the enterprise are shared on the computing server system, helping businesses make the best use of these resources and security, as well as optimizing financial resources, minimizing investment risks for fixed costs.

Built on a separate physical cluster, totally independent and unaffected by systems of other customers
Independent and private systems in Rated 3 – TIA 942 certified Data Centers of Viettel IDC ensure high safety and security
Easy to customize configuration and install system in accordance with actual needs via centralized and friendly administration tools
Saves time and costs for hardware, equipment and license. Customers may choose to own equipment after rental period
Is a new IT model in the IT field. This model allows the computational resource components in the data center to be combined into one physical resource cluster and the customer owns this resource and owns the benefits of cloud computing such as:
– The ability to quickly elastic
– Control of the service
Private Cloud can be deployed in a variety of ways, depending on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. Here are some common deployment models:
On-Premises Private Cloud (On-Premises Private Cloud):
– Characteristics: Cloud infrastructure is deployed and managed in the organization’s data centers.
– Advantages: Complete control over resources and data; highly secure because data does not leave the organization’s infrastructure.
– Disadvantages: High initial cost; complex management and maintenance requirements; need physical space and infrastructure.
Hosted Private Cloud (Private cloud hosting):
– Characteristics: Cloud infrastructure is deployed and managed by a cloud service provider, but resources are dedicated to a single organization.- Advantages: Reduce initial investment costs; no need to manage hardware and infrastructure; easily expandable.
– Disadvantages: Depends on service provider for security and performance; can be more costly in the long run.
Managed Private Cloud:
– Characteristics: The cloud service provider manages the entire infrastructure and services, including maintenance and technical support, while the organization still uses dedicated resources.
– Advantages: Easier management; Leverage service provider expertise; Reduce internal management burden.
– Disadvantages: Cost may be higher; depends on the vendor for security and management issues.
Assess needs and resources:Determine security, performance, and regulatory compliance requirements.
Assess available resources and financial capacity to deploy and maintain private cloud infrastructure.
Choose the appropriate deployment model:
Based on assessed requirements and resources, choose the most appropriate deployment model: on-premises, hosted, managed, or virtual.
Infrastructure architectural design:Determine required hardware and software configuration.
Plan for network, security, and data management requirements.
Deployment and configuration:Deploy hardware and software according to architectural design.
Configure cloud services and ensure integration with existing systems.
Management and maintenance:Set up routine management and maintenance procedures.
Ensure system updates and upgrades when necessary.
Track and monitor performance, security, and regulatory compliance.
Hardware:
Servers: Provide computing power to run applications and services.
Storage: Storage devices such as SAN (Storage Area Network) or NAS (Network-Attached Storage) to store data.
Networking: Networking devices such as switches, routers, and firewalls to connect and protect components in the system.
Software:
Operating System: Server operating system such as Linux or Windows Server to manage hardware.
Virtualization Software: Hypervisor such as VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, or KVM to create and manage virtual machines (VMs).
Cloud Management Software: OpenStack, VMware vCloud Suite, or Microsoft System Center to manage and automate cloud resources.
Networking:
SDN (Software-Defined Networking): Software-defined network solution that helps manage and configure networks flexibly and effectively.
VPN (Virtual Private Network): To ensure secure connection between Private Cloud components and remote users.
Security:
Firewall: Protects the system from unauthorized access.
IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems): Detect and prevent threats.
DLP (Data Loss Prevention): Prevent data loss and ensure data is not accessed illegally.
Management and Monitoring:
System Management Tools: Such as Nagios, Zabbix to monitor system performance and status.
Resource Management Tools: To manage resource allocation and usage.
Fill in the information in the table next to it and Viettel IDC staff will contact you soon!
Or call us now to learn more about service prices.
Hotline: 0966707701
Connect